The function calculates the face names that represent holes in a surface shape
Usage
holes(x, ...)
# S4 method for class 'trigrid'
holes(x, y, outside = FALSE)
# S4 method for class 'facelayer'
holes(x)Arguments
- x
(
trigrid,hexagridorfacelayer) An icosahedral grid or associated facelayer object.- ...
Arguments passed to class-specific methods.
- y
(
character) Horizontal shapes defined as a character vector of face names.- outside
(
logical) Should the set of faces that are outside the shape be returned as well?
Value
A named numeric vector, names correspond to faces, numbers outline the holes. If outside=FALSE and there are no holes in the shape, the function will return NULL.
Details
The function uses the horizontal graph of a trigrid-class object, removes the subgraph corresponding to a set of faces (the shape),
and searches for isolated subgraphs. The largest subgraph (highest number of vertices, i.e. faces) is considered to be outside of the shape.
This function relies on the igraph package to run.
Examples
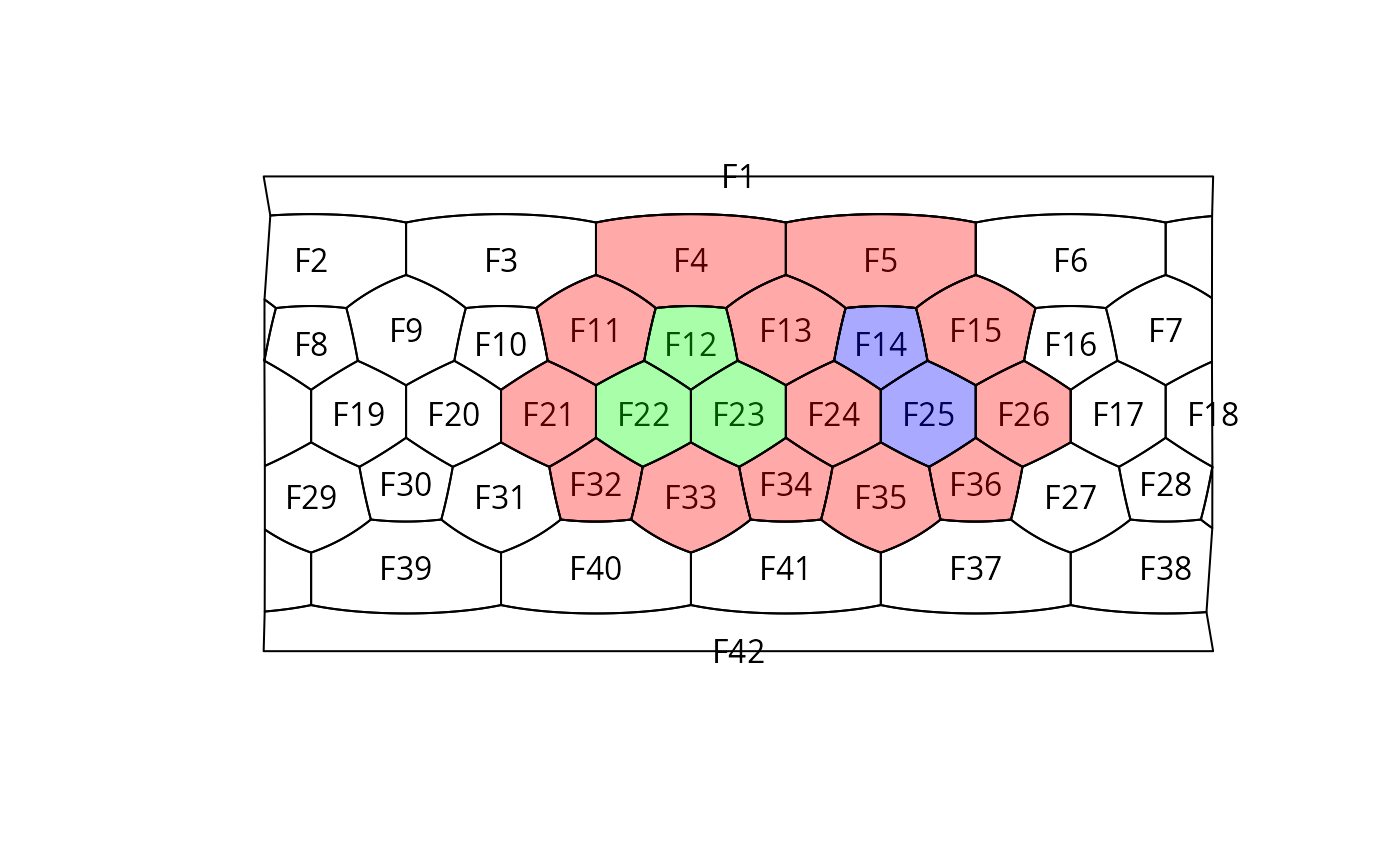
# create a grid
hex <- hexagrid(2, sf=TRUE)
# an example shape
shape <- paste0("F", c(4, 5, 11, 13, 15, 21, 24, 26, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36))
# visualize basic grid
plot(hex)
gridlabs(hex)
# visualize the shape
plot(hex, shape, col="#FF000055", add=TRUE)
# calculate holes
ho <- holes(x=hex, y=shape)
# plot both holes
plot(hex, names(ho[ho==1]), add=TRUE, col="#00FF0055")
plot(hex, names(ho[ho==2]), add=TRUE, col="#0000FF55")